The well equipped modern laboratory facilities at Oxford Brookes University have been developed to support a wide range of testing and development needs for industry and research. Tailored support is offered to meet clients’ needs and achieve compliance with codes and standards. It can develop products, systems, or approaches from initial design through to analysis, prototype testing, certification and delivery to market.
Architectural Technology Laboratory
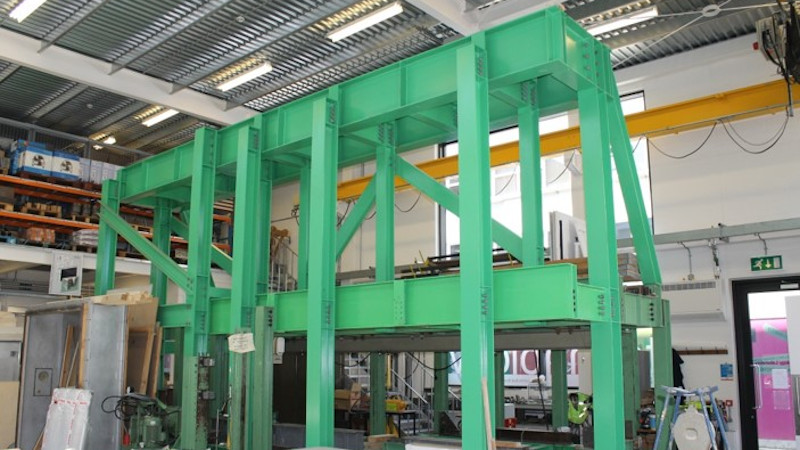
The central feature of the structural laboratory is a large reaction frame. This has been designed to accommodate a range of shapes and size of test specimen from purlins, joists or cladding panels up to 8m long to rectangular sections of wall or flooring system.
The majority of tests undertaken in this rig involve the application of either bending or compression loads to structural elements. However, a recent extension to the rig means that it is now also capable of undertaking racking tests on light steel or timber frame wall panels.
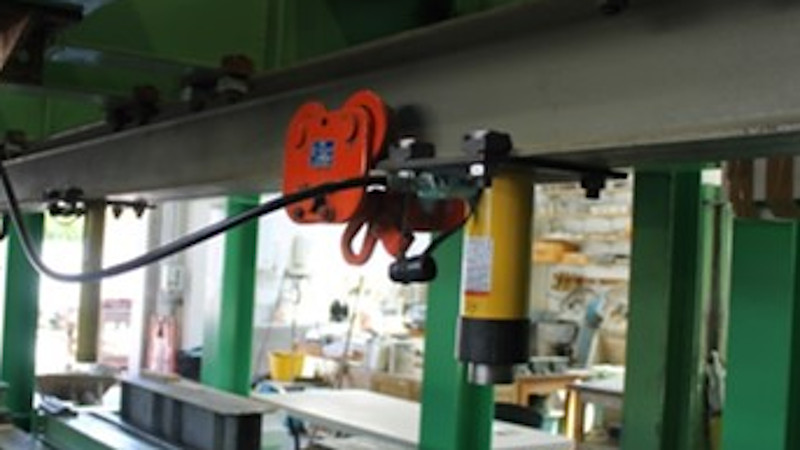


In all cases, loads are applied to the test specimen by one or more computer-controlled hydraulic jacks, ensuring precision loading at a pre-determined rate. Smaller products such as wall ties or brackets may be tested in tension or compression in one of the laboratory’s smaller testing machines. These machines may also be used to undertake shear tests on fastener assemblies.
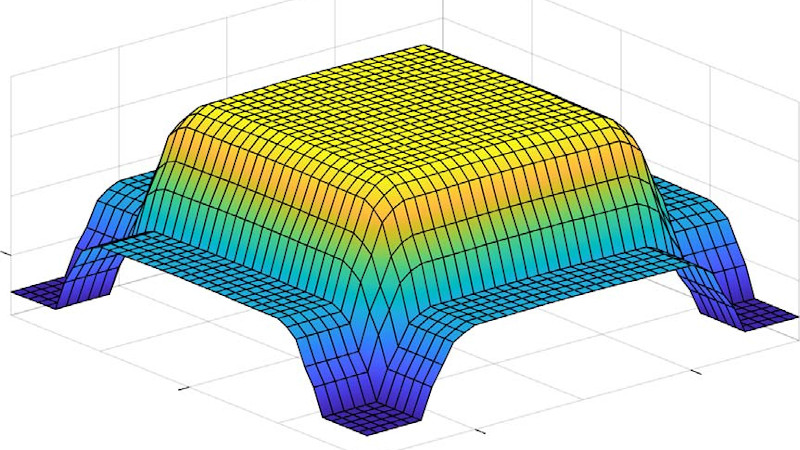
The VI Solar Simulator utilises a square array of halogen lamps and large reflection tube to uniformly illuminate samples up to 0.5m x 0.5m in area. The halogen lamps provide irradiance with a spectrum representative of solar spectral irradiance at Air Mass 1.5, in the range 200nm to 4000nm. Fans are installed to cool samples to counteract excess infrared radiation from the lamps.

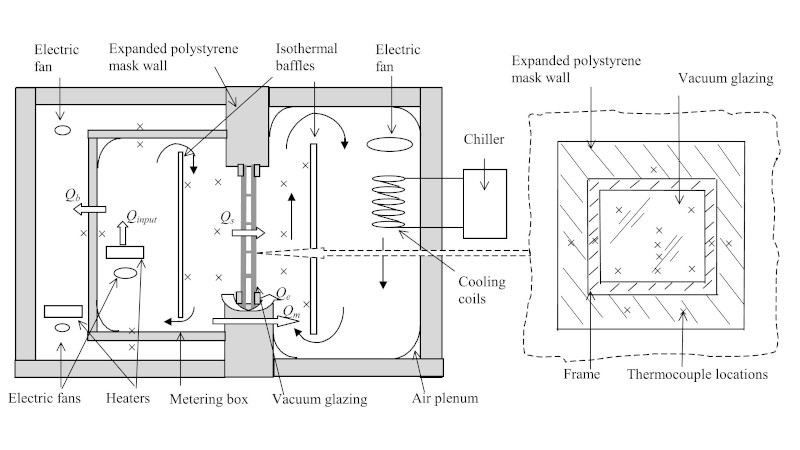
A new addition to the Oxford Brookes Architectural Technology Lab is a Guarded Hot Box (GHB) Calorimeter, designed and constructed in accordance with the recommendations of British and ISO standards, BS 8990. The GHB Calorimeter is capable of measuring the thermal insulating properties of building elements, such as composite panels, including measuring U-value. The GHB Calorimeter can test samples up to 1m x 1m in area and can create a 25C - 30C temperature difference across the sample.

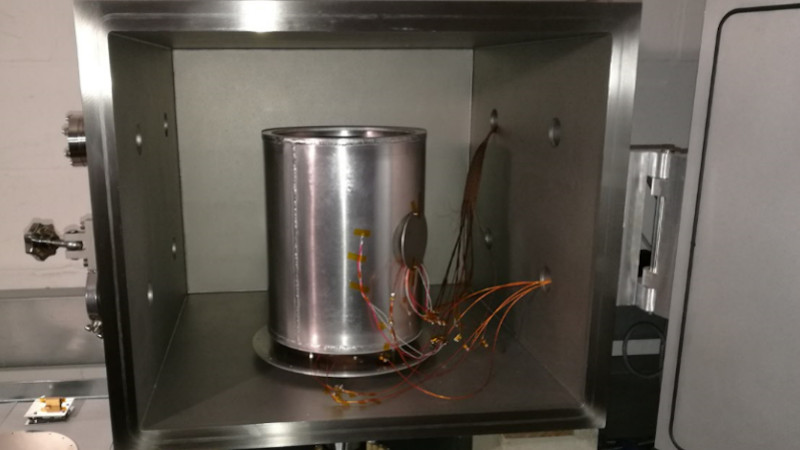
The Architectural Engineering Lab has a large volume cubic vacuum chamber (0.6m x 0.5m x 0.5m). The chamber has 8 vacuum feedthrough ports for power, fluids and sensors. The chamber is pumped via a turbomolecular vacuum pumping station and can achieve an ultimate vacuum pressure, in chamber, of 10-5 mbar.