Category: Non-domestic in-use building performance evaluation.
Objective: Widening our understanding of real energy performance in civic buildings.
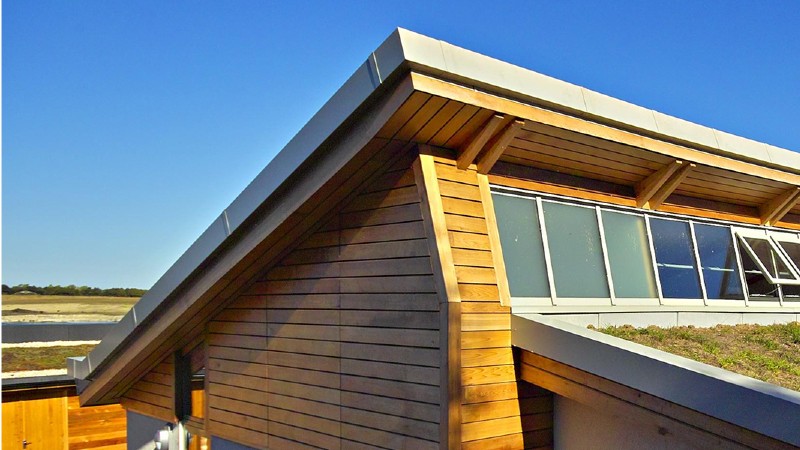
The building forms the main visitors centre at the College Lake nature reserve, run and managed by the Berks, Bucks and Oxon Wildlife Trust and gives vital teaching and office spaces for the Trust to communicate its message to the public.
The scheme is designed to a high environmental agenda and far exceed the building regulations. The building has been designed to be low energy based on ‘fabric first’ approach, focussing on elements such as airtightness, earth-retaining structure, high insulation levels, innovative rammed chalk material for internal walls, solar shading, thermal mass, stack ventilation system combined with 'high level' glazing and low energy fittings. The annual CO2 emission rate from the EPC is 23.37kg CO2/m2/year which is 50% less than the notional building of the same category.
This BPE study will verify the extent to which the design aspirations are met in reality and the reasons for the gap.
The areas of focus are (1) Effectiveness of ‘fabric first’ passive approach (2) Energy use compared to CIBSE, industry benchmarks using TM22 (3) Comfort criteria in office, meeting spaces with reference to summertime overheating (4) Performance of air-source heat pumps (5) The effect of the specified construction systems on moisture levels (6) The impact of the users on energy management and use.